Exploring the World of Edge Computing: Unleashing the Power of Proximity
Introduction
Definition of Edge Computing
Evolution from Cloud to Edge
Brief comparison with Cloud Computing
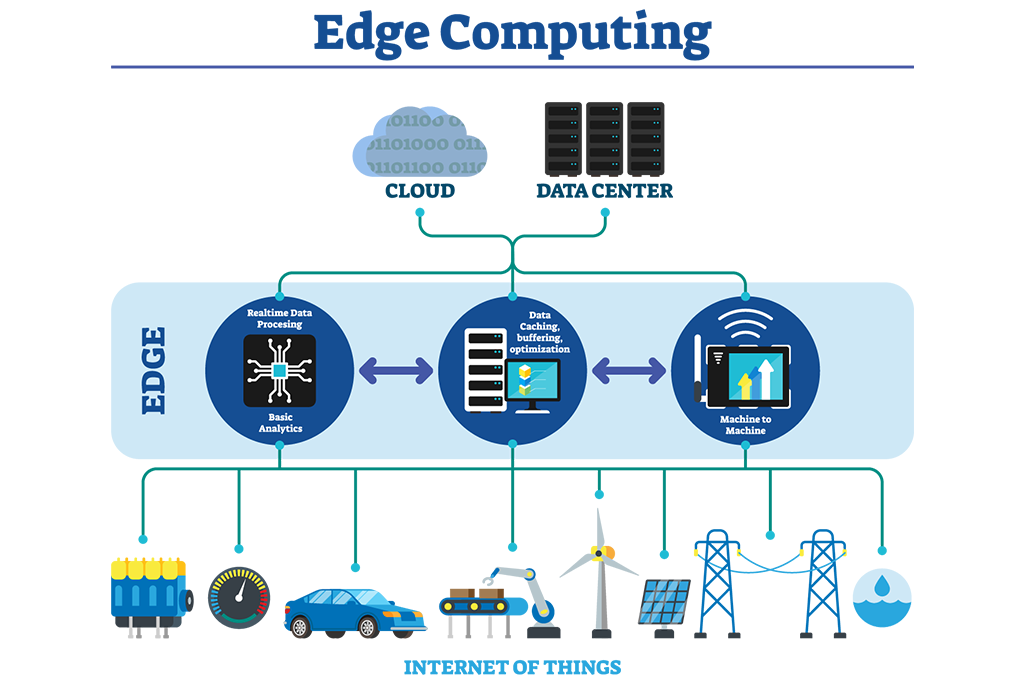
Understanding Edge Computing
1. Core Concepts
Decentralized Processing:
- Explanation of distributing computing power closer to data sources.
Real-time Data Processing:
Importance of immediate data analysis and response.
Examples of use cases benefiting from real-time processing.
2. Components of Edge Computing
Edge Devices:
Overview of devices at the edge (sensors, IoT devices, etc.).
Their role in collecting and generating data.
Edge Servers:
Description of local servers or gateways.
Processing capabilities near the data source.
Advantages of Edge Computing
1. Reduced Latency
Importance of low latency in applications.
Examples of industries benefiting from reduced latency.
2. Bandwidth Efficiency
Minimizing data transfer to the cloud.
Optimizing bandwidth usage for cost-effectiveness.
3. Enhanced Security and Privacy
Localized data processing for improved security.
Compliance with privacy regulations.
Use Cases
1. Industrial IoT
Predictive Maintenance:
- Monitoring equipment health in real-time.
Smart Factories:
- Automation and control at the edge.
2. Healthcare
Remote Patient Monitoring:
- Real-time health data analysis.
Medical Imaging:
- On-site processing for diagnostics.
3. Retail
Personalized Shopping Experiences:
- Real-time customer behavior analysis.
Inventory Management:
- Efficient supply chain operations.
Challenges and Solutions
1. Security Concerns
Overview of security challenges.
Implementing edge security measures.
2. Standardization
Lack of standardized edge computing protocols.
Efforts towards standardization.

Future Trends
Edge AI Integration:
Combining edge computing with artificial intelligence.
Improving decision-making capabilities.
5G and Edge:
- The synergy between 5G networks and edge computing.
Conclusion
Recap of the significance of edge computing.
The role it plays in shaping the future of technology.
